Global tech giants and major investors are pouring capital into cybersecurity startups, as the sector rapidly emerges as a “core strategic industry” driving both corporate competitiveness and national security. In just the first half of 2025, global cybersecurity startups attracted over ₩8 trillion (USD 6.4 billion) in funding.
Cybersecurity Startup Funding Up 14% in H1 — Google’s $32 Billion Acquisition of Wiz Marks a Landmark Deal

According to data from Pinpoint Search Group, 185 funding rounds were completed among cybersecurity vendors in the first two quarters of 2025, raising a total of USD 6.4 billion — a 14% increase compared to the same period last year.
Quarterly data shows a sharp upward trend: cybersecurity startup funding totaled USD 1.9 billion in Q2 2023, USD 2.3 billion in Q2 2024, and surged to USD 4.2 billion in Q2 2025. Notably, eight deals this year exceeded USD 100 million each, fueling this record growth.
A standout example is Cyera, an AI-driven data security startup that raised USD 540 million in a Series E round this June, bringing its total funding to over USD 1.3 billion. Founded in 2021, Cyera provides integrated security solutions that detect and respond to enterprise-wide data risks in real time.
OpenAI also made its first-ever cybersecurity investment in March, co-investing in Adaptive Security’s Series A round to counter AI-driven cyber threats rising alongside the spread of generative AI tools like ChatGPT. Silicon Valley VC giant Andreessen Horowitz joined the USD 43 million deal. Adaptive Security offers an AI-based social engineering simulation platform that helps organizations train and assess their defenses against realistic attack scenarios.
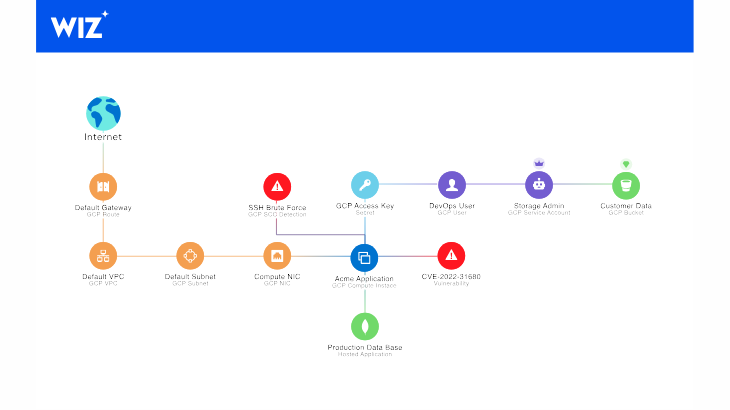
Meanwhile, global Big Tech companies are accelerating M&A in the cybersecurity space. The headline deal of 2025 was Google’s USD 32 billion acquisition of Wiz, marking the largest acquisition in Google’s history. Alphabet, Google’s parent company, cited the growing role of AI and the rapid adoption of cloud services as key motivations, noting that “cybersecurity has become vital to defending against new risks and safeguarding national security.” Wiz provides an integrated cloud security platform compatible with all major cloud and code environments and counts AWS, Microsoft, and Google among its major clients.
In Korea, Coontec, a convergence and supply chain security company, recently raised a Series A round from Hyosung Ventures and NH Investment & Securities. Another Korean firm, S2W, successfully debuted on KOSDAQ this month — its IPO price doubled from ₩13,200 to ₩26,000 on opening day, later peaking at ₩40,000 within a week.
Escalating Cyber Threats Trigger Massive Capital Inflows

The surge in cybersecurity investments is being driven by increasingly sophisticated and frequent cyberattacks amid rapid digital transformation.
According to a report by Korea’s Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Internet & Security Agency (KISA), the number of reported cyber incidents in H1 2025 reached 1,034 cases, up 15% from 899 cases a year earlier. The information and communications sector accounted for 32% of all incidents, with a 29% year-on-year increase.
Major cyber incidents in the first half of 2025 included the large-scale SIM information breach at SK Telecom, ransomware attacks targeting online bookstore Yes24 and insurer SGI Seoul Guarantee, and multiple hacks of domestic and international cryptocurrency exchanges.
Attackers are evolving alongside defense technologies—employing increasingly intelligent and evasive tactics. Emerging threat types include supply chain attacks, credential-stuffing attacks, and new forms of malware. In recent years, cryptocurrency exchanges have become prime targets of supply chain attacks, as hackers exploit vulnerabilities in less-secure vendors or third-party services rather than attacking well-protected core systems directly.
Credential-stuffing remains a persistent issue, where stolen account credentials traded on the dark web are used to attempt logins across multiple platforms. Because many users reuse similar passwords across sites, one breach can cascade into widespread secondary damage.
New strains of malware are also appearing — such as Antidot, which abuses Android accessibility privileges to gain remote control of devices, and Godfather, which uses virtualization to mimic legitimate banking apps and steal account information. Both are engineered to evade detection by traditional security tools.
◆ New Malware “EvilAI” Disguised as Finder, OneStart, or PDF Editor

A recent report by U.S. cybersecurity firm Trend Micro warns of a new AI-powered malware dubbed “EvilAI.” The malware blends sophisticated social engineering with AI-generated legitimate code, allowing it to infiltrate systems, evade detection, and maintain persistent access.
EvilAI disguises itself under innocuous names such as Manual Finder, One Start, or PDF Editor — masquerading as genuine productivity or AI-enhancement software. According to Trend Micro, “EvilAI uses a professional-looking interface and valid digital certificates to deceive users and security tools alike, making it almost indistinguishable from legitimate applications.”
Telemetry data shows the malware spreading rapidly, with the highest infection rates reported across Europe, the Americas, and the AMEA region (Asia, Middle East, and Africa).
Samsung SDS Identifies Top 5 Cyber Threats for 2025 — AI-Driven Phishing and Ransomware Top the List
Samsung SDS analyzed global cybersecurity incidents from the past year and identified five key threats for 2025: ▲AI-enabled phishing attacks ▲Cloud security vulnerabilities ▲Ransomware attacks ▲Software supply chain compromises ▲OT/IoT security risks
The company warned that the proliferation of generative AI and the shift toward cloud-based infrastructure have amplified phishing and cloud-related security threats. Misconfigured cloud settings, exposed long-term credentials, and outdated security versions were cited as major causes.
Ransomware continues to evolve into double extortion schemes, combining data encryption with information theft and blackmail. The rise of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) platforms allows attackers without deep technical knowledge to easily launch large-scale attacks.
The growing reliance on open-source software has also increased the risk of malicious code infiltrating software supply chains. As companies increasingly integrate third-party components into their systems, they face heightened exposure to embedded vulnerabilities.
Finally, Samsung SDS highlighted escalating threats to Operational Technology (OT) and Internet of Things (IoT) systems. With factories, connected devices, and wearables forming vast hyperconnected networks, outdated OT/IoT devices have become prime targets for hackers.
Jang Yong-min, Executive Director of Cybersecurity at Samsung SDS, emphasized:
“AI-driven security threats are becoming more intelligent and deceptive. Enterprises must adopt organization-wide crisis management strategies that encompass not only AI-based intelligent security solutions and tailored cloud configurations, but also rigorous access control, partner ecosystem management, and regular system updates.”
